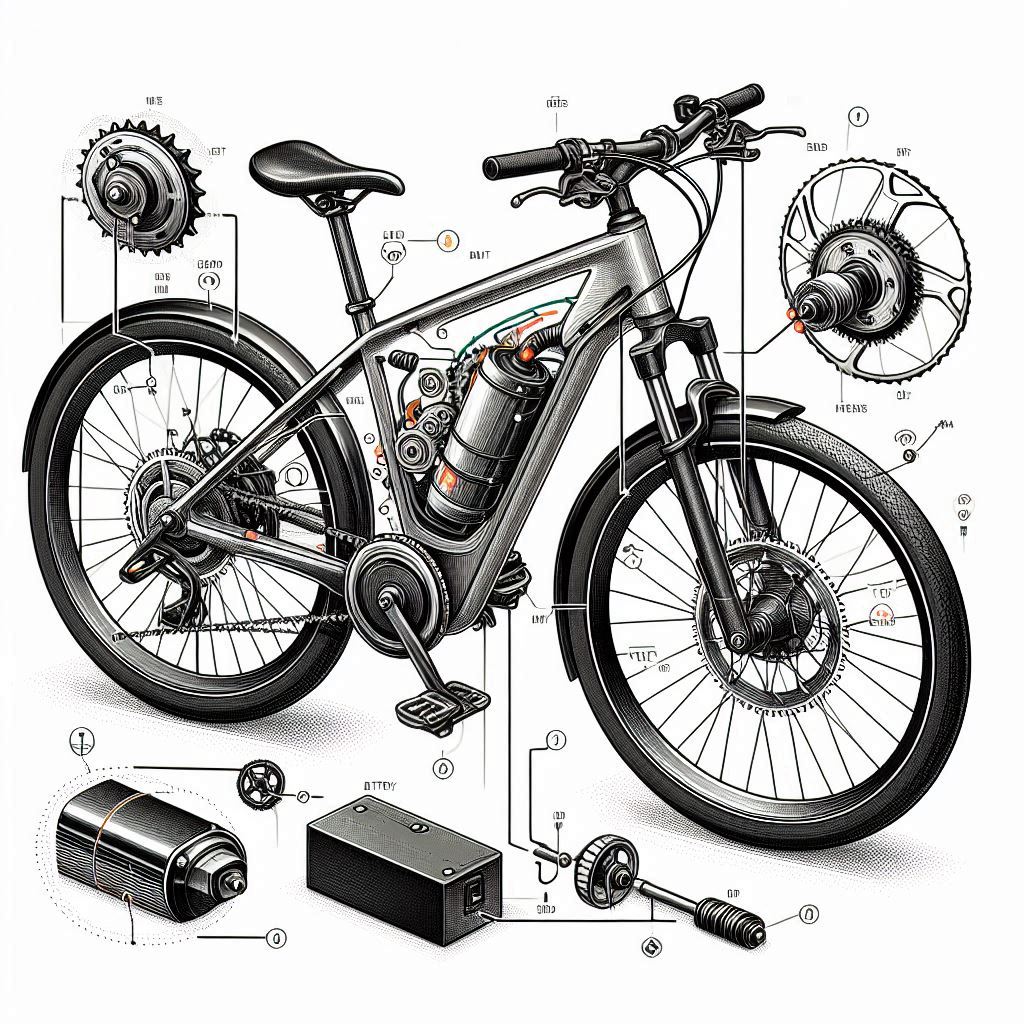
Electric Bike Components Glossary
Last Updated on August 8, 2024 by Kristina Grant
The essential parts that make up your e-bike are the motor, battery, display, tires, and brakes.
Motor
The motor is the heart of an electric bike, providing the propulsion. There are two main types of e-bike motors: hub motors and mid-drive motors. Hub motors are located in the wheel hub, while mid-drive motors are located in the center of the bike
Hub motors
- Advantages: Simple design, lower cost, and easier maintenance.
- Disadvantages: Less efficient than mid-drive motors, can be less powerful, and can be more difficult to pedal when the motor is off.
Mid-drive motors
- Advantages: More efficient than hub motors, can be more powerful, and can be easier to pedal when the motor is off.
- Disadvantages: More complex design, higher cost, and more difficult to maintain.
Battery
The battery stores the energy that powers the e-bike motor. Battery capacity is measured in watt-hours (Wh). Higher watt-hour capacity batteries will provide a longer range on a single charge.
Battery types
- Lithium-ion: The most common type of battery used in e-bikes. They are lightweight, have a high energy density, and have a long lifespan.
- Lead-acid: A less common type of battery used in e-bikes. They are heavier, have a lower energy density, and have a shorter lifespan.
- Nickel-metal hydride: A type of battery that is no longer commonly used in e-bikes. They are heavier, have a lower energy density, and have a shorter lifespan.
Display
The display shows information about the e-bike, such as speed, battery level, and pedal assist mode. Displays can be LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) or LED (Light-Emitting Diode).
RELATED CONTENT – Top 3 Ebike Displays with Largest Screens
LCD displays
- Advantages: More energy-efficient, can be more durable, and can be more colorful.
- Disadvantages: Can be more difficult to read in direct sunlight.
LED displays
- Advantages: Can be more readable in direct sunlight, can be more durable, and can be less expensive.
- Disadvantages: Can be less colorful and less energy-efficient.
Tires
The tires are the contact point between the bike and the ground. They are made of rubber and have a tread pattern that helps to grip the road.
Tire types
- Slick tires: These tires have no tread pattern and are designed for use on smooth surfaces, such as pavement.
- Tread tires: These tires have a tread pattern that helps to grip the road in wet or dry conditions.
- Knobby tires: These tires have a deep tread pattern that helps to grip the road in off-road conditions.
Brakes
The brakes are used to slow down or stop the bike. There are two main types of brakes: disc brakes and rim brakes. Disc brakes are more powerful and reliable than rim brakes.
Disc brakes
- Advantages: More powerful, more reliable, and can be used in wet or dry conditions.
- Disadvantages: More expensive and more complex to maintain.
Rim brakes
- Advantages: Less expensive and simpler to maintain.
- Disadvantages: Less powerful, less reliable, and can be less effective in wet conditions.
Frame
The frame is the main structure of the bike, often made of aluminum, steel, or carbon fiber. It is the backbone of the bike and all other components are attached to it.
Fork
The fork is the front suspension component, which can be rigid or have suspension. It is attached to the frame and holds the front wheel.
Chain
The chain connects the pedals to the rear wheel. It is a key component of the drivetrain and is responsible for transferring power from the rider to the rear wheel.
RELATED CONTENT – Ebike Chain Maintenance
Cassette
The cassette is a cluster of gears on the rear wheel. It allows the rider to change gears and adjust the bike’s speed and power.
Derailleur
The derailleur is the mechanism that shifts the chain between gears. It is operated by the rider using the shifters on the handlebars.
Saddle
The saddle is the seat of the bike. It is where the rider sits and provides support for the back and legs.
Handlebars
The handlebars are the control levers for steering and braking. They are also used to operate the shifters and other controls.
Stem
The stem connects the handlebars to the fork. It allows the rider to adjust the height and angle of the handlebars.
Pedals
The pedals are the platforms for the rider’s feet. They are used to apply power to the bike and to control the bike’s direction.
Fenders
The fenders are optional components that protect the rider from water and debris. They are typically mounted on the front and rear wheels.
Lights
The lights are optional components that provide visibility in low-light conditions. They are typically mounted on the front and rear of the bike.
Racks
The racks are optional components that are used to carry cargo. They are typically mounted on the front and rear of the bike.
If you can’t find the term you’re looking for, please leave a comment below and we’ll add it.
Kristina Grant is not just an enthusiast but a true authority on electric bikes. Nestled in the coastal beauty of Virginia, Kristina has found the perfect backdrop for her passion for electric biking. As a dedicated wife and homeschooling mom, her life revolves around family, faith, and the thrill of adventure.
Originally hailing from Ohio, Kristina's journey with electric bikes began as a curiosity and quickly evolved into a deep expertise. Her blog is a testament to her love for electric biking, combining her fascination for eco-friendly transportation with her coastal lifestyle.
When she's not cruising the beach on her electric bike, you'll find Kristina indulging in her other loves: long walks along the shore, getting lost in a good book, and cherishing moments with her loved ones. With a heart as big as her love for animals, especially cats, Kristina brings a unique perspective to the electric bike world, grounded in her strong faith in God and her dedication to a sustainable lifestyle.
Through her blog, Kristina shares her extensive knowledge of electric bikes, offering valuable insights, tips, and recommendations to fellow enthusiasts. Whether you're a seasoned rider or a newcomer to the electric bike scene, Kristina's blog is your go-to source for all things electric biking, fueled by her passion, expertise, and the scenic beauty of coastal Virginia.